Commercial Solar
Commercial solar may seem straightforward solar for businesses as opposed to residential solar for homes. However, commercial solar encompasses a variety of different types of customers and projects. In addition to businesses of different sizes, from large corporations to local small businesses, “commercial” solar customers can also include governments, schools and universities, and even nonprofits.

Solar PPA
A solar power purchase agreement (PPA) is a financial agreement where a developer arranges for the design, permitting, financing and installation of a solar energy system on a customer’s property at little to no cost. PPAs typically range from 10 to 25 years and the developer remains responsible for the operation and maintenance of the system for the duration of the agreement. At the end of the PPA contract term, a customer may be able to extend the PPA, have the developer remove the system or choose to buy the solar energy system from the developer.
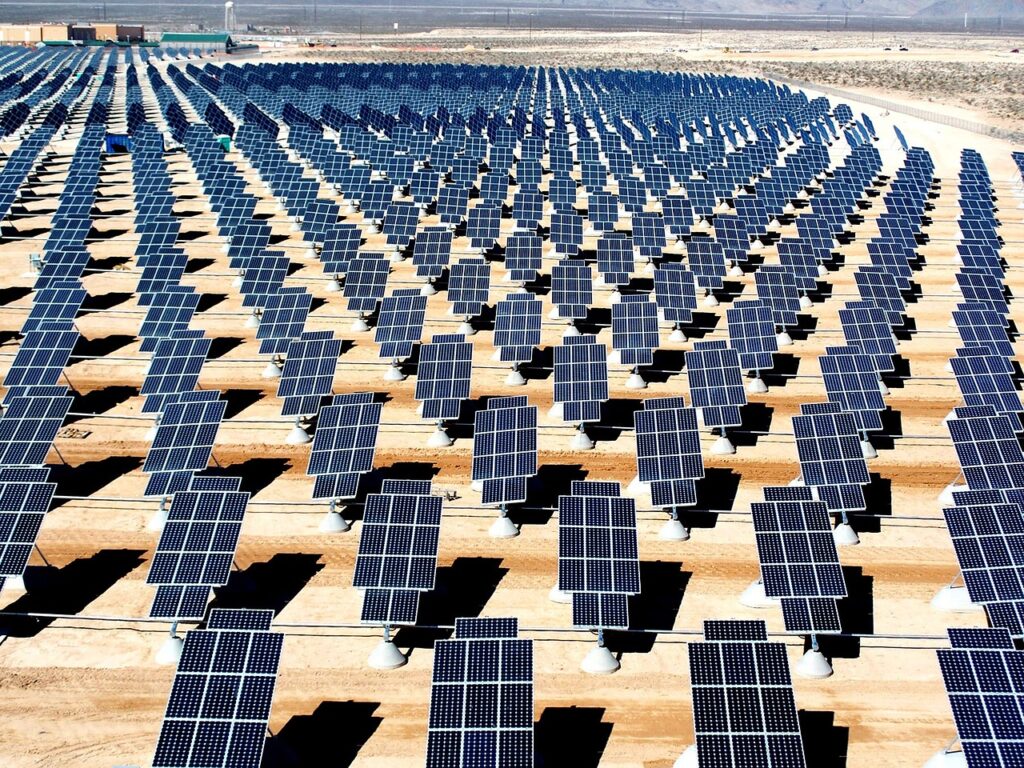
Solar Farms
A solar farm is a large collection of photovoltaic (PV) solar panels that absorb energy from the sun, convert it into electricity and send that electricity to the power grid for distribution and consumption by customers like you. Solar farms — which you’ll sometimes see being called solar parks or photovoltaic power stations — are usually mounted to the ground instead of rooftops and come in all shapes and sizes.


Energy Rebates
The following are questions and answers regarding the Home Energy Rebates administered by the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE) and funded by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). For more information, please visit the Home Energy Rebates page.
Air Conditioning
Three-quarters of all homes in the United States have air conditioners. Air conditioners use about 6% of all the electricity produced in the United States, at an annual cost of about $29 billion to homeowners. As a result, roughly 117 million metric tons of carbon dioxide are released into the air each year. To learn more about air conditions, explore our Energy Saver 101 infographic on home cooling.Air conditioners employ the same operating principles and basic components as your home refrigerator.

Some Other Services

Residential Solar/ Commercial Solar
Company owners and homeowners are increasingly looking to switch to solar energy. There are four major aspects of solar energy systems that determine whether they’re commercial or residential: efficiency, size, installation, and color.
Commercial CHP
Combined heat and power (CHP), or cogeneration, offers a range of potential benefits for commercial applications such as offices, retail developments, mixed use developments and district energy schemes. Commercial CHP systems are successfully applied in a range of different applications including office buildings, airports and retail centres.Where there is a local demand for cooling, combined cooling heat and power technology, also called trigeneration may provide added benefits.


Energy Rebats
Tune-ups help keep your HVAC systems running safely and efficiently, reducing your operating costs and keeping your facility comfortable in any weather. They also help extend the life of existing HVAC systems and can help your business avoid costly repairs.
Solar PV

Solar Frams
Battery Storage
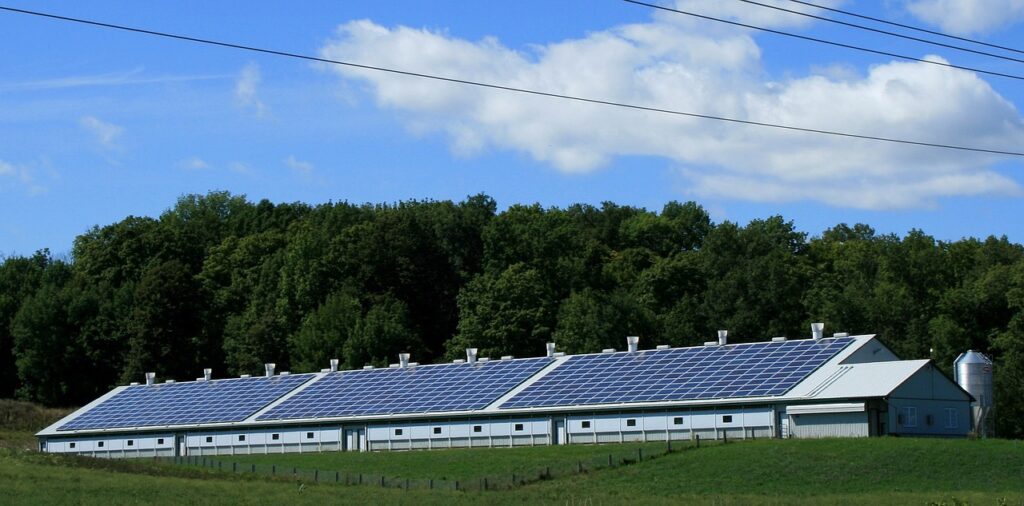

Soalr PPA

Covering Residential and Commertial
ECO4 Grants Separates
Funding is available to cover all the cost of energy efficiency measures. Some of the most common measures are Panel Heaters to Electric Storage Heaters, loft insulation, Cavity wall insulation Internal wall insulation, Room in Roof Insulation, FTCH First Time Central Heating etc.


Heat Pumps and Gas Boilers
Here’s how the two are fundamentally different: A heat pump operates by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it inside your home. A traditional boiler, on the other hand, uses natural gas, propane, or heating oil to create heat which is then circulated through your home’s pipes.
Air Conditioning
Three-quarters of all homes in the United States have air conditioners. Air conditioners use about 6% of all the electricity produced in the United States, at an annual cost of about $29 billion to homeowners. As a result, roughly 117 million metric tons of carbon dioxide are released into the air each year. To learn more about air conditions, explore our Energy Saver 101 infographic on home cooling.Air conditioners employ the same operating principles and basic components as your home refrigerator. Refrigerators use energy (usually electricity) to transfer heat from the cool interior of the refrigerator to the relatively warm surroundings of your home;


CHP
CHP technology can be deployed quickly, cost-effectively, and with few geographic limitations. CHP can use a variety of fuels, both fossil- and renewable-based. It has been employed for many years, mostly in industrial, large commercial, and institutional applications. CHP may not be widely recognized outside industrial, commercial, institutional, and utility circles, but it has quietly been providing highly efficient electricity and process heat to some of the most vital industries, largest employers, urban centers, and campuses in the United States.
How We Help to Reduce the Cost And Become More Energy Efficient

Getting EPC grades from G-A

Help Commercial Landloads

Minimal Cost






